Back braces may be recommended for children and adolescents with small to moderate curves (up to 40 degrees) who are still growing. They are especially beneficial during growth spurts. In many cases they can slow down or stop progression of curves, potentially avoiding the need for surgery. There are various types of braces, and they are more effective the more hours per day that they are worn.
The Rigo Cheneau brace is one type of brace successfully used at Neuro Spinal Hospital. It is made of a light plastic material moulded to a patient’s shape. These types of braces are custom made for each individual patient to apply corrective pressure to the selected areas to slow progression of, or even partially correct, spinal curves and rotations. Rigo Cheneau braces are designed to provide comfort, room for growth, and minimal restriction of movement. They are usually worn for 16-24 hours per day until a child stops growing.
Physiotherapy with scoliosis-specific exercises can help to strengthen the muscles of the back to better support the spine and improve posture. This type of therapy is often recommended in conjunction with bracing.
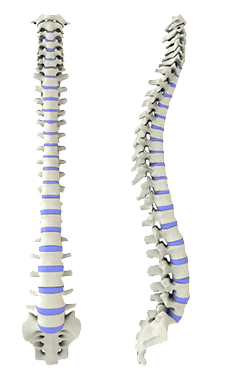
Spinal Fusion is the standard surgical procedure for scoliosis. This involves using metal rods, hooks and screws to hold the vertebrae (bones of the spine) in a corrected position to reduce the curvature and stop it getting worse. A bone graft is placed into the spaces between the vertebrae so that, over the following months, the bones grow together to form a solid bone.
Spinal fusion surgery is often performed via an incision down the middle of the back (posterior) but may also be done via an anterior approach, from the front or side.
Spinal fusion is a well-established procedure with a long-term record for safety and efficacy. Fusion of bone stops the part of the spine which is operated on growing. There may be some loss of flexibility in the area, but this is usually small and does not affect everyday activities.
Growing rods may be used to stabilize the spine in growing children who are too young for spinal fusion. They are attached to the spine and lengthened as a child grows. MAGEC™ (MAGnetic Expansion Control), is a magnetically driven rod, which can be lengthened without additional surgical procedures. Spinal fusion may be required when growth has stopped.